The need for robust project management practices has never been more critical. Establishing a Project Management Office (PMO) is a strategic move that can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to deliver projects successfully, on time, and within budget. This briefing explores the essential steps and best practices for setting up a PMO that aligns with organizational goals and drives project excellence.
If your focus is dollars and cents, read the PMO cost brake down to learn about the costs of a PMO based on industry data for best practices.
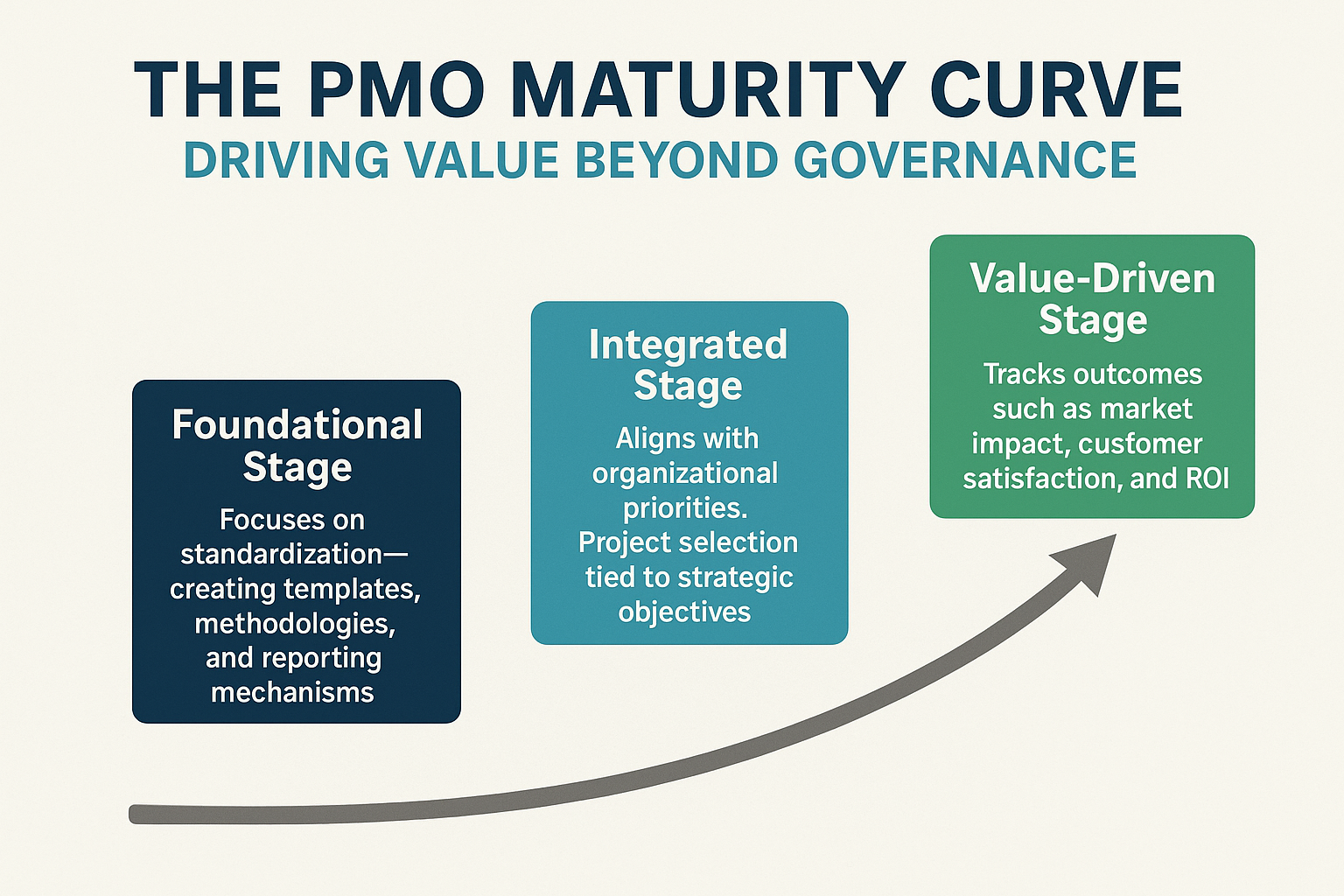
Introduction
The establishment of a Project Management Office (PMO) marks a pivotal point in an organization’s project management journey. A well-structured PMO provides the framework and governance executives needed to ensure projects are executed effectively, resources are utilized efficiently, and strategic objectives are met. This briefing delves into the key components of PMO setup, from defining its structure and roles to implementing best practices that foster a culture of project success.
Defining the PMO Structure
The foundation of a successful PMO lies in its structure. A clear and well-defined execution structure outlines the PMO’s scope, authority, and responsibilities, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- PMO Charter: The PMO charter is a critical document that defines the PMO’s purpose, scope, and objectives. It serves as the guiding beacon for all PMO activities and establishes the authority and governance framework necessary for effective project oversight.
- PMO Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are essential for the PMO’s success. This includes identifying key positions such as the PMO Director, Project Managers, and support staff, along with their specific duties and reporting lines.
- PMO Framework: Developing a comprehensive PMO framework involves selecting appropriate methodologies and tools that align with the organization’s project management needs. This framework should include standardized processes for project initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure.
Implementing Best Practices
To ensure the PMO delivers value, it is crucial to adopt best practices that promote consistency, efficiency, and continuous improvement.
- Project Governance: Effective project governance involves establishing policies and procedures that guide project execution and decision-making. According to PMI’s Pulse of the Profession® report, organizations with strong governance frameworks are 20% more likely to complete projects successfully.
- PMO Roadmap: A PMO roadmap outlines the strategic initiatives and milestones necessary for the PMO’s development and growth. This roadmap should be aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives and regularly reviewed to track progress and adapt to changing needs.
- Stakeholder Communication: Building strong communication channels with stakeholders is vital for the PMO’s success. Regular updates, transparent reporting, and active engagement with stakeholders ensure alignment and foster trust.
Achieving PMO Excellence
The journey to establishing a PMO is not without challenges, but the rewards are substantial. A well-established PMO can drive project success, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall organizational performance.
- PMO Best Practices: Adopting industry best practices, such as those outlined by the Project Management Institute (PMI), can provide valuable guidance and benchmarks for PMO success. As noted by Harold Kerzner in “Project Management Best Practices: Achieving Global Excellence,” successful PMOs continuously refine their processes and adapt to new project management trends.
- PMO Strategy: Developing a clear PMO strategy that aligns with the organization’s long-term goals is essential. This strategy should include performance metrics to measure the PMO’s impact and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Establishing a PMO is a strategic initiative that requires careful planning, clear structure, and the adoption of best practices. By defining its charter, roles, and framework, and by implementing strong governance and stakeholder communication, organizations can lay the foundation for a PMO that drives project success and delivers significant value. Continuous improvement and alignment with strategic goals ensure that the PMO remains a vital component of the organization’s project management capabilities.
References
- Pulse of the Profession® | Project Management Institute
- Project Management Best Practices: Achieving Global Excellence | Harold Kerzner, 2018
- The PMO Lifecycle: Building, Running, and Shutting Down | Bill Dow, Bruce Taylor, 2015
- The Strategic Project Leader | Jack Ferraro, 2012
This briefing provides a guide to establishing a PMO, ensuring that organizations are equipped with the knowledge and strategies needed to build a strong foundation for project success.